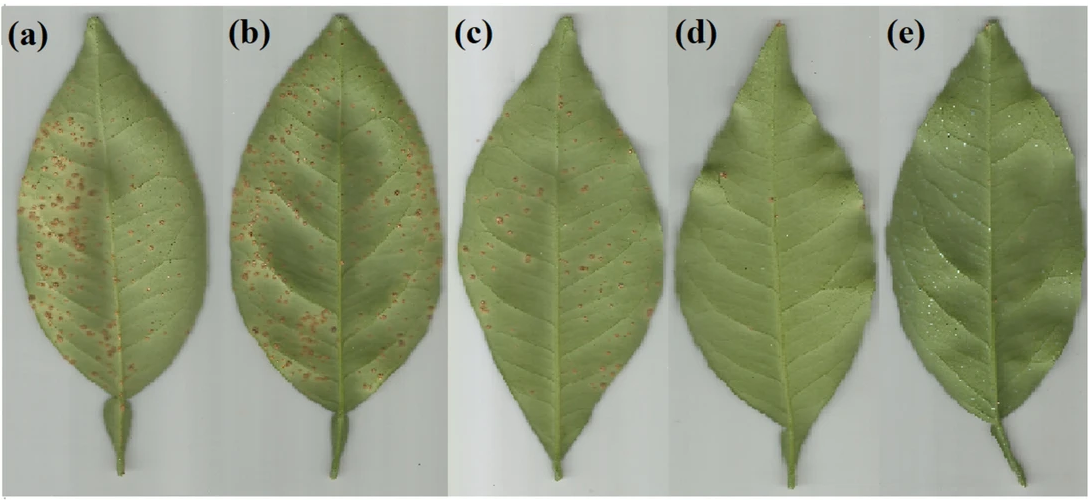
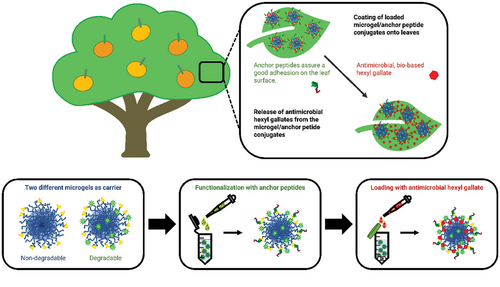
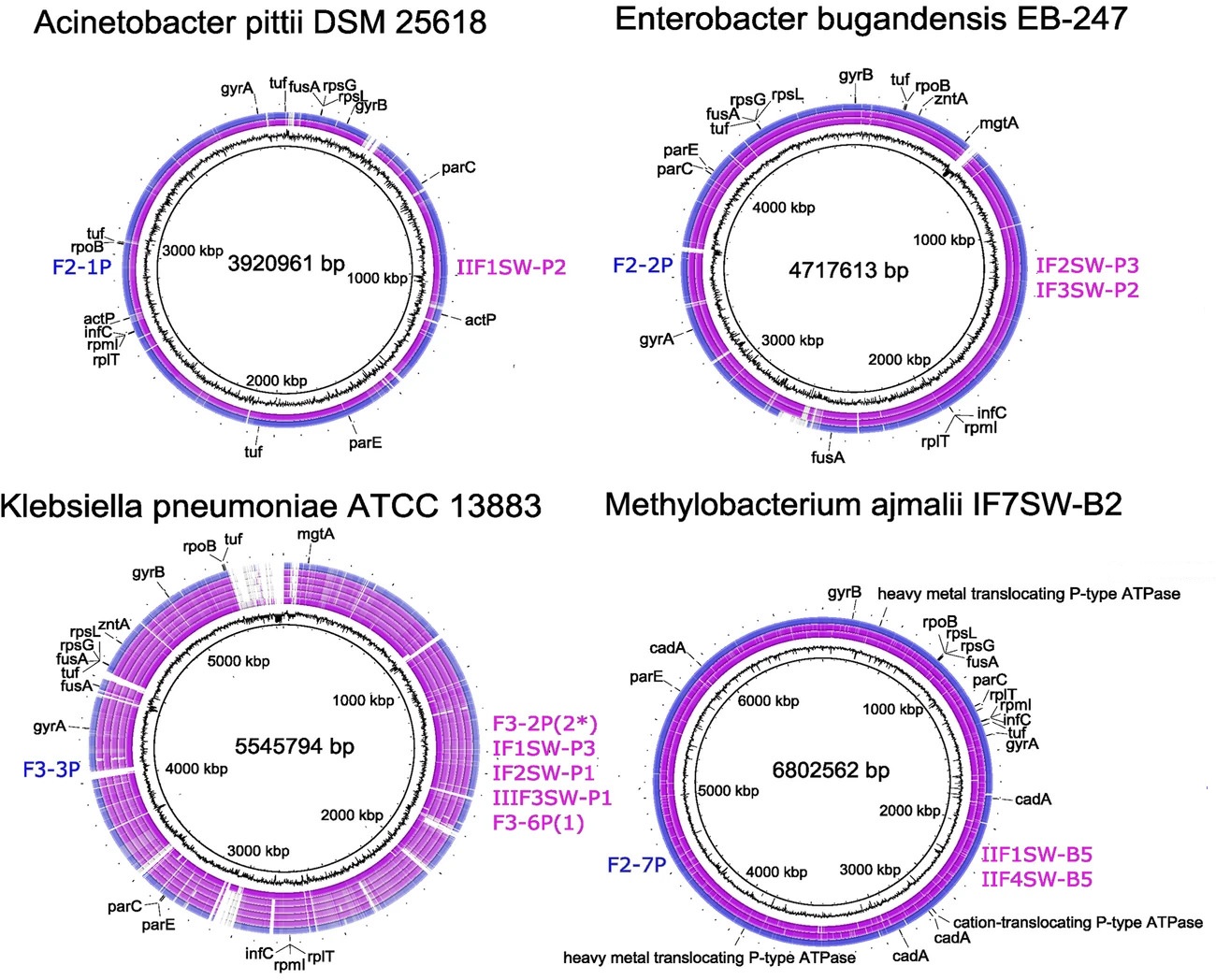
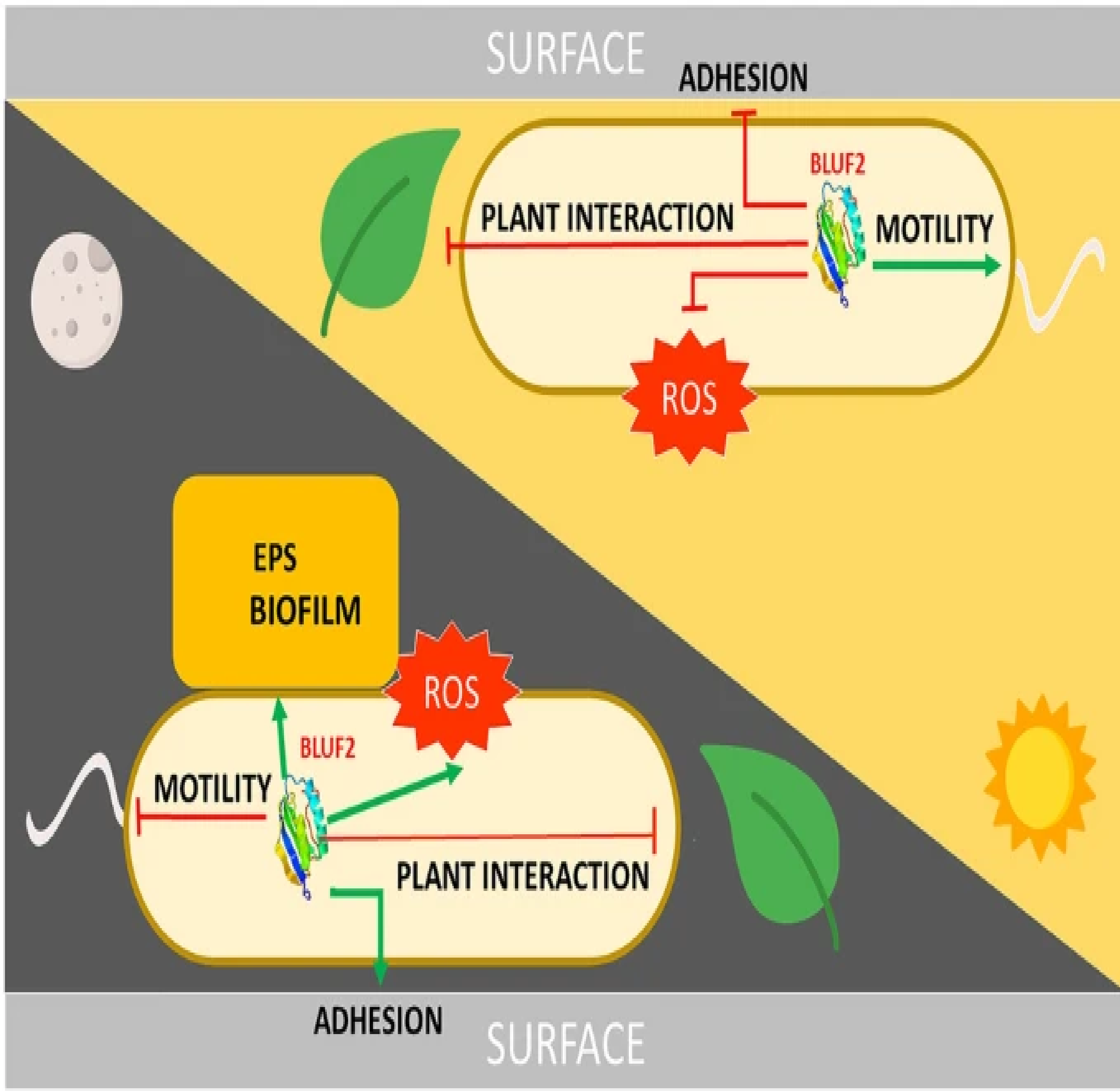
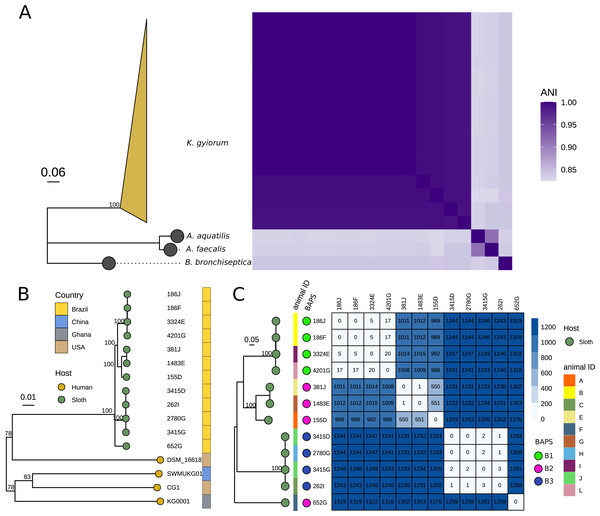
Bifunctional peptides as alternatives to copper‐based formulations to control citrus canker
Citrus canker is an infectious bacterial disease and one of the major threats to the orange juice industry, a multibillion-dollar market that generates hundreds of thousands of jobs worldwide. This…